
|
Cococubed.com
|
|
Detonation Density Effects on White Dwarf Supernovae |
Home
Astronomy research
Software Infrastructure:
MESA
FLASH-X
STARLIB
MESA-Web
starkiller-astro
My instruments
Neutrino Emission:
Neutrinos from de-excitation
Neutrino emission from stars
Identifying the Pre-SN
Neutrino HR diagram
Pre-SN Beta Processes
Pre-SN neutrinos
White dwarf pulsations:
12C(α,γ) & overshooting
Probe of 12C(α,γ)16O
Impact of 22Ne
Impact of ν cooling
Variable white dwarfs
MC reaction rates
Micronovae
Novae
White dwarf supernova:
Stable nickel production
Remnant metallicities
Colliding white dwarfs
Merging white dwarfs
Ignition conditions
Metallicity effects
Central density effects
Detonation density
Tracer particle burning
Subsonic burning fronts
Supersonic fronts
W7 profiles
Massive stars:
Pop III with HST/JWST
Rotating progenitors
3D evolution to collapse
MC reaction rates
Pre-SN variations
Massive star supernova:
Yields of radionuclides
26Al & 60Fe
44Ti, 60Co & 56Ni
SN 1987A light curve
Constraints on Ni/Fe
An r-process
Effects of 12C +12C
Neutron Stars and Black Holes:
Black Hole spectrum
Mass Gap with LVK
Compact object IMF
He burn neutron stars
Stars:
Hypatia catalog
SAGB stars
Nugrid Yields I
He shell convection
BBFH at 40 years
γ-rays within 100 Mpc
Iron Pseudocarbynes
Pre-Solar Grains:
C-rich presolar grains
SiC Type U/C grains
Grains from massive stars
Placing the Sun
SiC Presolar grains
Chemical Evolution:
Radionuclides in 2020s
Zone models H to Zn
Mixing ejecta
Thermodynamics, Opacities & Networks
Radiative Opacity
Skye EOS
Helm EOS
Five EOSs
Equations of State
12C(α,γ)16O Rate
Proton-rich NSE
Reaction networks
Bayesian reaction rates
Verification Problems:
Validating an astro code
Su-Olson
Cog8
Mader
RMTV
Sedov
Noh
Software Instruments
2026 AAS Journals
AAS YouTube
Listing of 500+ Author Videos
AAS Peer Review Workshops
Outreach Material
Education Material
Other Stuff:
Bicycle Adventures
Illustrations
Presentations
Contact: F.X.Timmes
my one page vitae,
full vitae,
research statement, and
teaching statement.
Evaluating Systematic Dependencies Of Type Ia Supernovae: The Influence Of Deflagration To Detonation Density (2010)
In this article we explore the effects of the deflagration to detonation transition (DDT) density on the production of $^{56}$Ni in thermonuclear supernova (SN) explosions (Type Ia supernovae).
Within the DDT paradigm, the transition density sets the amount of expansion during the deflagration phase of the explosion and therefore the amount of nuclear statistical equilibrium (NSE) material produced. We employ a theoretical framework for a well-controlled statistical study of two-dimensional simulations of thermonuclear SNe with randomized initial conditions that can, with a particular choice of transition density, produce a similar average and range of $^{56}$Ni masses to those inferred from observations. Within this framework, we utilize a more realistic "simmered" white dwarf progenitor model with a flame model and energetics scheme to calculate the amount of $^{56}$Ni and NSE material synthesized for a suite of simulated explosions in which the transition density is varied in the range (1 - 3) $\times$ 10$^7$ g cm$^{-3}$.
We find a quadratic dependence of the NSE yield on the log of the transition density, which is determined by the competition between plume rise and stellar expansion. By considering the effect of metallicity on the transition density, we find the NSE yield decreases by 0.055 $\pm$ 0.004 M$_{\odot}$ for a 1 Z$_{\odot}$ increase in metallicity evaluated about solar metallicity. For the same change in metallicity, this result translates to a 0.067 $\pm$ 0.004 M$_{\odot}$ decrease in the $^{56}$Ni yield, slightly stronger than that due to the variation in electron fraction from the initial composition. Observations testing the dependence of the yield on metallicity remain somewhat ambiguous, but the dependence we find is comparable to that inferred from some studies.
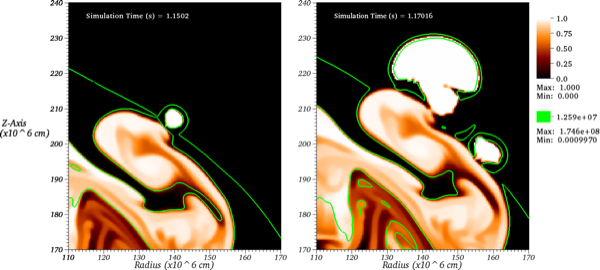
|

|

|

|
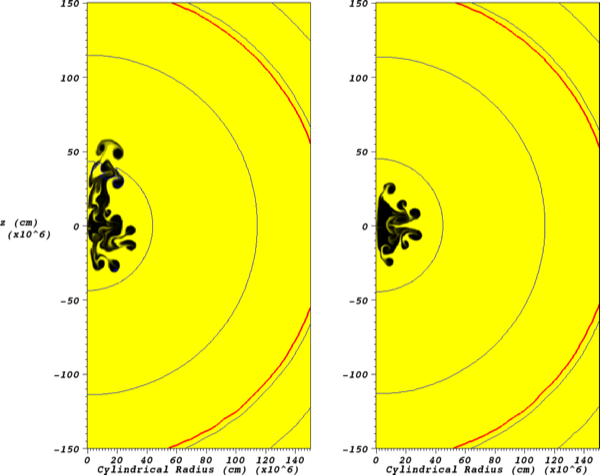
early deflagration phases |

|